Introduction
Knee cartilage injuries can lead to discomfort and challenges in movement. The cartilage in your knee acts like a cushion, protecting your joint from friction and impact. When this cartilage gets damaged, it can cause pain and affect your ability to walk, run, or engage in your daily activities. Let’s explore what knee cartilage is, how injuries can happen, and how you can manage and prevent them.
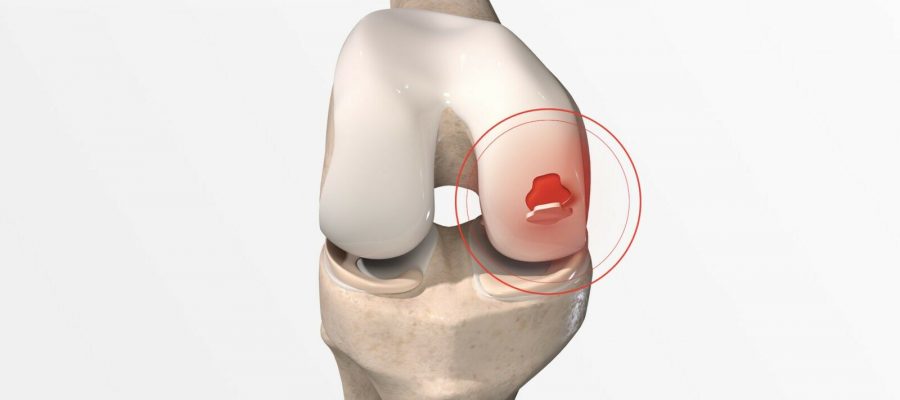
What is Knee Cartilage?
Imagine your knee joint as a complex puzzle with bones fitting together. Cartilage is the smooth, rubbery material that covers the ends of these bones, preventing them from rubbing against each other. It acts like a protective layer, allowing your knee to move smoothly and without pain.
Common Causes of Cartilage Injuries
Knee cartilage injuries can happen due to various reasons:
Impact:
A direct blow to the knee, like falling on it or getting hit, can damage the cartilage.
Age:
As you get older, the cartilage might become weaker and more prone to injuries.
Repetitive Movements:
Activities that involve frequent bending and straightening of the knee can lead to wear and tear of the cartilage over time.
Sports:
High-impact sports or those that involve sudden stops and starts can increase the risk of cartilage injuries.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Cartilage injuries can cause several symptoms:

Stiffness:
The knee might feel stiff and limited in its range of motion.
Catching or Locking:
Some people might feel a clicking or catching sensation when they move their knee.
Pain:
You might experience pain, especially when putting weight on the knee or moving it.
Swelling:
The knee can become swollen due to inflammation.
Your knee specialist will likely perform a physical examination, ask about your symptoms and activities, and may use imaging tests like X-rays or MRI to diagnose the extent of the injury.
Treatment and Recovery
Treatment options depend on the severity of the injury:
Rest and Pain Relief:
For minor injuries, resting the knee and using over-the-counter pain medications can help manage symptoms.
Physiotherapy:
A physiotherapist or fitness trainer can guide you through exercises that strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve joint stability.
Injections:
In some cases, your doctor might recommend injections of substances that can help with pain and inflammation.
Surgery:
For severe injuries, surgery might be necessary to repair or remove damaged cartilage.
Preventing Cartilage Injuries
While some injuries might be unavoidable, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk:
Maintain Healthy Weight:
Carrying excess weight can put extra stress on your knee, increasing the risk of injuries.
Stay Active:
Regular exercise can help keep your muscles strong, providing better support to your knee joint.
Use Proper Techniques:
Whether you're exercising or lifting heavy objects, using the right techniques can prevent strain on your knee.
Wear Protective Gear:
If you're engaging in sports, using appropriate protective gear can help reduce the risk of injury.
Conclusion
Knee cartilage injuries can be challenging, but with proper care and treatment, you can manage your symptoms and work towards recovery. If you suspect a cartilage injury, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and guidance on treatment. By taking steps to prevent injuries and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, you can prioritize your knee’s well-being and continue enjoying your daily activities.



