Overview
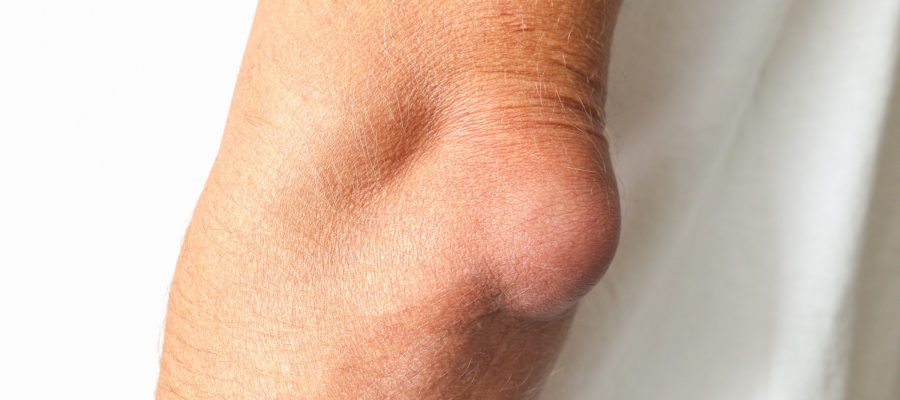
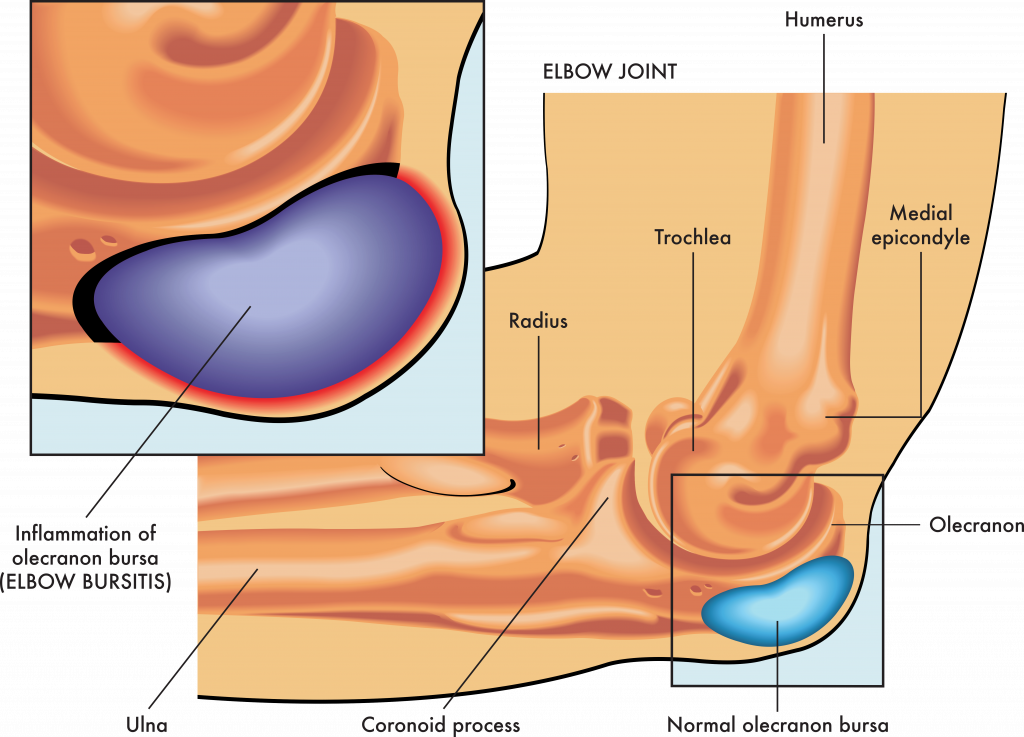
Elbow bursitis, also called olecranon bursitis, occurs when the bursa at the tip of the elbow becomes inflamed. The olecranon is the pointed bone forming the elbow’s tip, and the bursa is a fluid-filled sac that sits between the bone and the skin. Its function is to allow the skin to move smoothly over the bone without friction. When the bursa becomes irritated or inflamed, it can swell and enlarge, leading to a condition known as bursitis.
Causes of Elbow Bursitis
Elbow bursitis occurs when the bursa, a small fluid-filled sac located at the tip of the elbow, becomes inflamed. This inflammation can cause pain, swelling, and limited movement in the joint. The main causes of elbow bursitis include:
- Prolonged pressure: Repeated pressure on the elbow, such as leaning on hard surfaces, can irritate the bursa over time.
- Injury: A direct blow or trauma to the elbow can lead to inflammation of the bursa.
- Infection: Bacteria entering through a cut or scrape near the elbow may infect the bursa, causing it to become inflamed.
- Repetitive motions: Activities that involve frequent bending and extending of the elbow can strain the bursa.
- Underlying conditions: Medical conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and gout can increase the risk of developing elbow bursitis.
If you experience persistent swelling or pain in your elbow, it’s important to consult a doctor for evaluation and treatment.
Symptoms & Signs
Common symptoms and signs of elbow bursitis include:
Swelling at the back of the elbow.
Pain when it first swells, after a direct impact or when the patient rests their elbow on a hard surface while it is swollen.
Hot and red skin over the swollen region.
Fever (occasionally).
Orthopaedic Assessment
At Total Orthopaedic Care & Surgery (TOCS), the orthopaedic assessment would include a detailed history of any symptoms, physical examination, and initial imaging tests such as X-rays. Further imaging with an MRI or ultrasound may also be required to investigate the cause of the elbow swelling.
Elbow Bursitis Treatment Options
Treatment for olecranon bursitis will depend on several factors such as age, cause of symptoms, size of swelling, duration of symptoms and lifestyle impacts. Non-surgical options such as rest, an armsling, ice and anti-inflammatory medications can help relieve pain and speed up recovery. In some cases, a needle may be used to drain fluid from the elbow bursa if it is suspected to be infected. This fluid will then be sent to the laboratory for analysis and antibiotics may be started.
Surgery
In situations where the bursa does not self-resolve or is infected, surgery may be required. This could involve removing most or all of the bursa tissue. At TOCS, where appropriate, our orthopaedic specialists prefer to perform minimally-invasive excisions (endoscopic excision) of the olecranon bursa. This involves using cameras and shavers to remove the affected tissue.

Conclusion
It is important to follow your orthopaedic specialist’s instructions for treatment and rehabilitation in order to obtain the best possible outcome for your elbow swelling. If you have olecranon bursitis and would like to consider minimally-invasive surgery, do make an appointment with our orthopaedic specialist at TOCS for a detailed assessment of your condition.




