Introduction
Knee osteoarthritis is a common condition that affects your knee joint, causing pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. It’s important to understand what osteoarthritis is and how it can be managed to maintain good knee health and improve your quality of life.
What is Knee Osteoarthritis?
Knee osteoarthritis is a type of arthritis that specifically impacts the knee joints. Arthritis is a term used to describe the inflammation and degeneration of joints over time. In knee osteoarthritis, the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones in your knees starts to wear down, leading to pain and discomfort.
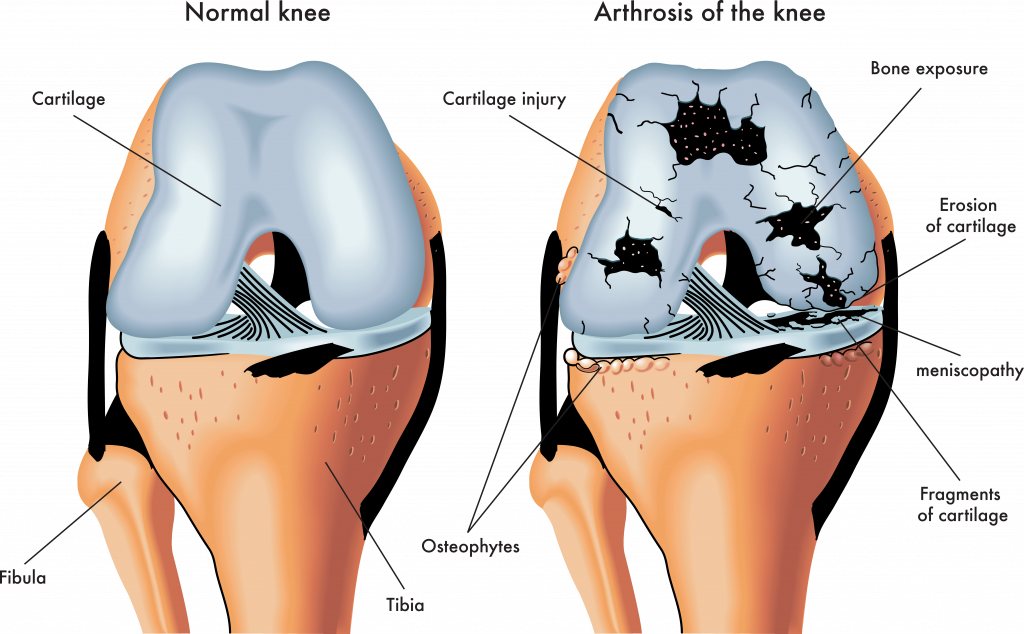
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of knee osteoarthritis:
Age:
As we grow older, the natural wear and tear on our joints can increase the risk of osteoarthritis.
Weight:
Carrying excess weight or having unhealthy body weight places additional stress on the knees, accelerating the breakdown of cartilage.
Joint Injuries:
Previous knee injuries, such as fractures or ligament tears, can increase the likelihood of developing osteoarthritis.
Genetics:
If osteoarthritis runs in your family, you might be at a higher risk.
Gender:
Women are more likely than men to develop knee osteoarthritis.
Stiffness:
Feeling stiff or having difficulty moving your knee, especially after periods of rest.
Symptoms
The symptoms of knee osteoarthritis can vary from person to person, but common signs include:
Pain:
Persistent pain in the knee joint, especially during or after movement.
Swelling:
Swelling around the knee joint due to inflammation.
Stiffness:
Feeling stiff or having difficulty moving your knee, especially after periods of rest.
Reduced Range of Motion:
Finding it hard to fully bend or straighten your knee.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis begins with a detailed assessment, which includes a physical examination to check for pain, swelling, and reduced range of motion. Imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs are typically used to confirm the extent of joint degeneration and identify any other related knee issues.
Treatment Options
Non-Surgical Treatment Options:
For mild to moderate cases, non-surgical osteoarthritis treatment can help manage pain and slow the progression of the disease. Treatment options include lifestyle modifications such as weight management and low-impact exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee. Medications, including anti-inflammatories and pain relievers, are often prescribed to alleviate discomfort. Additionally, hyaluronic acid or corticosteroid injections may be used to lubricate the joint and reduce inflammation. Physiotherapy also plays a key role in improving mobility and strengthening the knee.
Surgical Treatment Options:
In more advanced cases where non-surgical methods are insufficient, surgery may be necessary. Our team offers knee osteoarthritis surgery options, including partial or total knee replacement, depending on the severity of joint damage. Minimally invasive procedures like arthroscopy can be used to clean out debris and smooth rough cartilage, while more severe cases may require joint replacement surgery to restore function and relieve pain.
For those seeking effective osteoarthritis treatment in Singapore, our specialists at Total Orthopaedic provide personalised care, focusing on improving quality of life and promoting long-term joint health.
Managing Knee Osteoarthritis
While knee osteoarthritis cannot be completely cured, there are steps you can take to manage your symptoms and improve your joint health:
Exercise:
Engaging in low-impact exercises, such as walking, exercising on the elliptical machine or cross-trainer, swimming, or cycling, can help strengthen the muscles around your knee and improve joint flexibility.
Pain Relief:
Over-the-counter pain medications or topical creams can help manage pain and inflammation. Consult your doctor before starting any new medication.
Use Adjunct Devices:
Adjunct devices like braces or walking aids can provide additional support to your knee and alleviate pain during movement.
Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Losing excess weight can significantly reduce the stress on your knee joints.
Physiotherapy:
A physiotherapist or a fitness trainer can design exercises and stretches tailored to your condition to improve your knee's range of motion and stability.
Hot and Cold Therapy:
Applying heat or cold packs to your knee can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Healthy Diet:
Consuming foods rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids can support joint health. Foods like fruits, vegetables, fish, and nuts are great options.
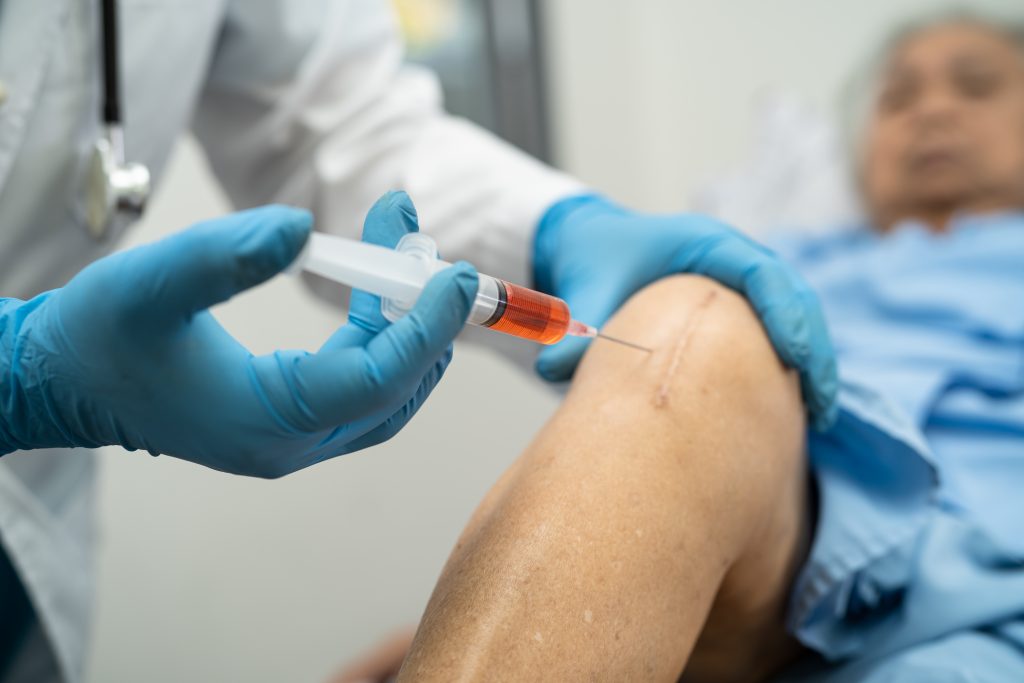
When to Seek Medical Help
If you experience severe pain, sudden swelling, or any significant changes in your symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. We at Total Orthopaedic Care & Surgery offer comprehensive knee oesteoarthritis treatment in Singapore, offering both surgical and non-surgical solutions tailored to each patient’s needs.
Conclusion
Knee osteoarthritis is a common condition that can cause discomfort and impact your daily life. However, with the right strategies and lifestyle changes, you can manage your symptoms effectively and maintain good joint health. Remember to stay active, maintain a healthy weight, and seek medical advice when needed to ensure you’re taking the best care of your knees. We are always here should you need us!




