Latarjet Procedure
The Latarjet procedure is a surgical technique used to treat shoulder instability, particularly in cases where there is significant bone loss (15-20%) in the glenoid (the shallow socket of the shoulder blade where the ball of the upper arm bone fits).
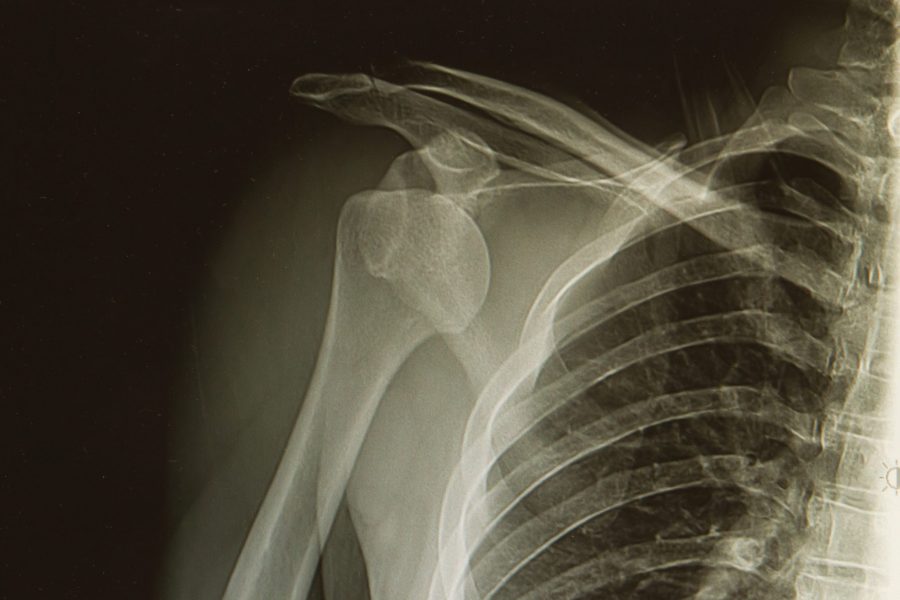
This procedure involves transferring a piece of bone with attached muscles and tendons from the coracoid process (a bony projection on the anterior shoulder blade) to the front of the shoulder joint, where it is fixed in place with screws or small buttons.

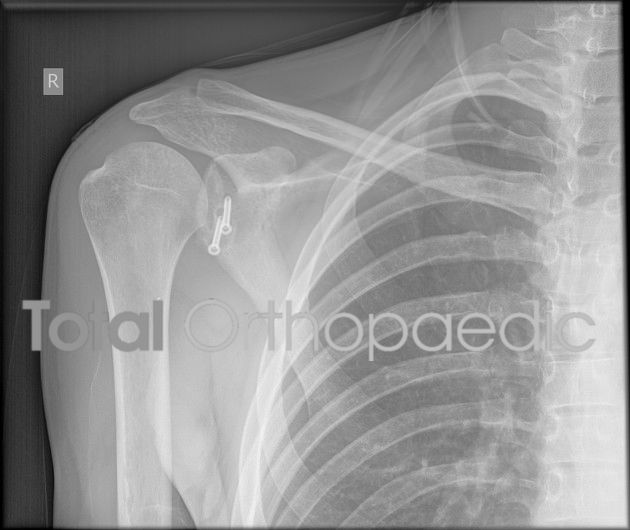
The Latarjet procedure can provide stability to the shoulder joint and prevent dislocations by creating a larger, more stable surface for the ball of the upper arm bone to rest in. Indications for it include recurrent shoulder dislocations/instability episodes or as a primary treatment for instability in young athletes, especially those that participate in contact sports.
Like any surgery, the Latarjet procedure has its risks. These include infection, bleeding, nerve damage and failure of the bone graft to heal or unite with the glenoid surface. Recovery time can vary depending on the extent of the procedure and individual factors, but typically involves a short period of immobilization followed by a rehabilitation program to restore strength and range of motion in the shoulder. It is important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of the Latarjet procedure with your doctor before deciding whether it is the right treatment option for you.
Here at Total Orthopaedic Care & Surgery, Our Surgeon’s preference would be the use of small buttons and sutures (novel) for the Latarjet procedure as it has some benefits.
If you suspect you have shoulder instability, would like it assessed and seek a comprehensive discussion on your management options, including a Button and Suture Latarjet procedure, do make an appointment with our orthopaedic specialist at Total Orthopaedic Care & Surgery for a detailed assessment and discussion of your condition today.
Please note that the provided content is for informational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice.




